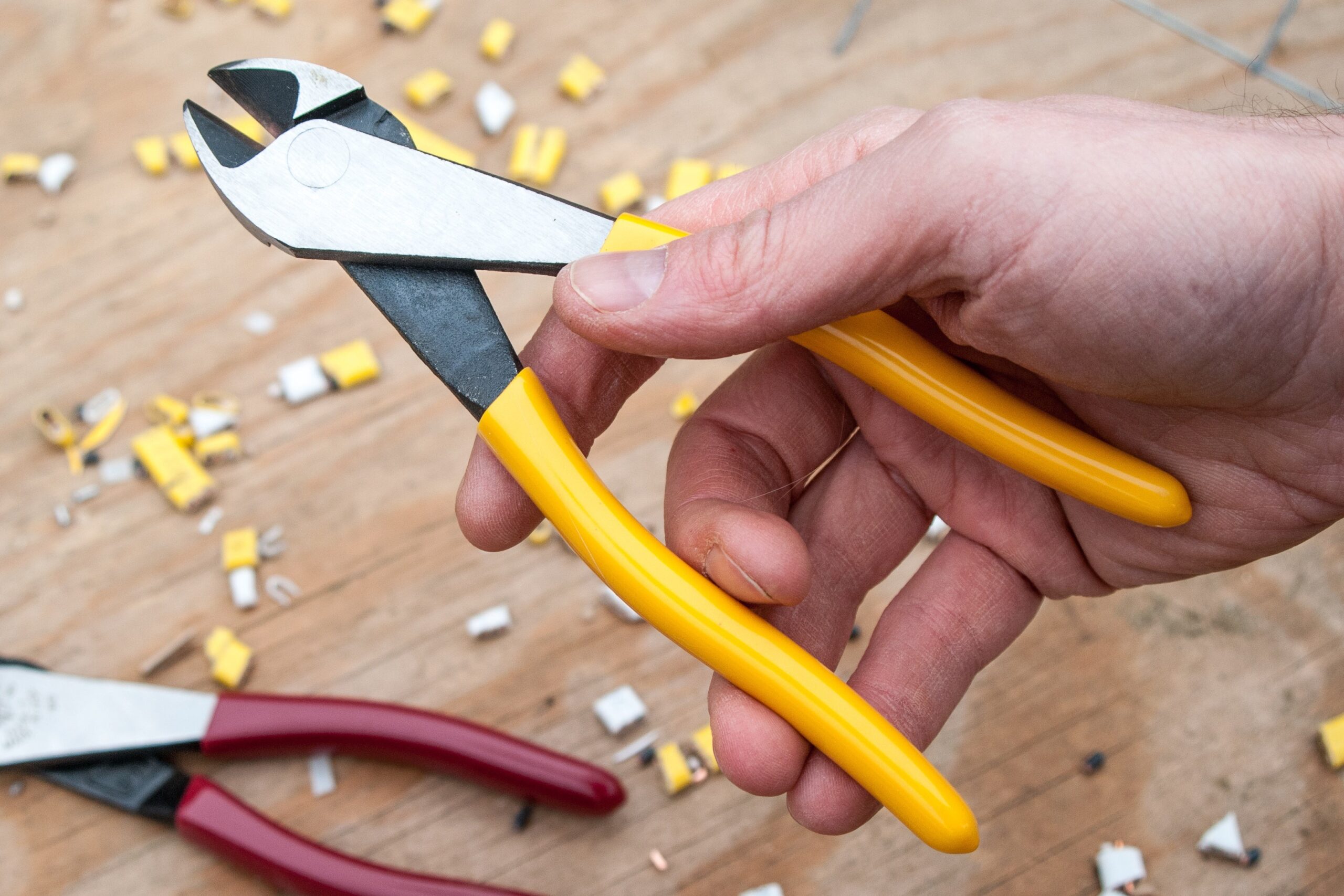
In various fields ranging from electrical work to crafting, a wire cutter is an “Wire Cutter” indispensable tool. Despite its seemingly simple design, this tool plays a crucial role in countless tasks, offering precision and efficiency when dealing with wires, cables, and other similar materials. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a DIY enthusiast, understanding the nuances of wire cutters can significantly enhance your workflow.
This comprehensive guide will delve into everything you need to know about wire cutters, from the types available and how to select the right one for your needs, to tips on proper usage and maintenance. By the end of this article, you’ll be equipped with all the knowledge necessary to make an informed decision and keep your wire cutter in top condition.
1. What is a Wire Cutter?
A wire cutter, also referred to as a wire snip or pliers, is a tool specifically designed to cut wires and cables. Its primary function is to provide a clean, precise cut through various types of wires, whether they are made of copper, aluminum, steel, or other materials. Wire cutters are commonly used in electrical work, crafting, construction, and automotive repair, among other fields.
Key Features of a Wire Cutter:
- Cutting Edges: Typically made from hardened steel to withstand the cutting of tough materials.
- Handles: Ergonomically designed for comfort and ease of use, often covered with rubber or plastic for better grip.
- Spring Mechanism: Some wire cutters feature a spring-loaded mechanism that opens the jaws automatically after a cut, reducing hand fatigue during prolonged use.
- Locking Mechanism: Certain models come with a lock to keep the cutter closed when not in use, ensuring safety.
Wire cutters are versatile tools that can handle a variety of tasks, making them essential in both professional and home environments.
2. Types of Wire Cutters
Wire cutters come in several different types, each designed to handle specific tasks. Understanding these types will help you choose the right tool for your needs.
a. Diagonal Wire Cutters
Diagonal wire cutters are among the most commonly used types. The cutting edges are angled, allowing them to cut through wires by pushing them apart. These cutters are ideal for cutting small gauge wires, such as those used in electrical wiring and small crafts.
Uses:
- Cutting small electrical wires.
- Trimming excess wire in electronic projects.
- Snipping wire ties and cable ties.
b. End-Cutting Pliers
End-cutting pliers have a flat, blunt end that allows for flush cuts close to surfaces. This design is particularly useful for removing nails, staples, or other fasteners.
Uses:
- Removing fasteners like nails and staples.
- Cutting wires flush against a surface.
- Pruning small branches in gardening.
c. Cable and Wire Rope Cutters
Cable and wire rope cutters are designed to handle thicker cables and wire ropes. They often feature a ratcheting mechanism that provides additional cutting power, making it easier to cut through tough materials without excessive force.
Uses:
- Cutting large electrical cables.
- Trimming wire ropes in construction and rigging.
- Cutting through steel cables used in fencing.
d. Specialty Wire Cutters
Specialty wire cutters are designed for specific tasks that require unique cutting capabilities. Examples include bolt cutters, which are used to cut through bolts and chains, and precision wire cutters, which are ideal for delicate electronic work.
Uses:
- Cutting bolts, chains, and padlocks (bolt cutters).
- Trimming fine wires in electronics (precision wire cutters).
- Cutting through hardened materials like piano wire.
3. How to Choose the Right Wire Cutter
Selecting the right wire cutter is crucial for ensuring efficient and safe operation. Here are the factors to consider when choosing a wire cutter:
a. Material of the Wire
The material of the wire you plan to cut is a significant factor in choosing the right wire cutter. Different materials require different cutting edges:
- Copper and Aluminum: These are soft metals, so most wire cutters can handle them without issues.
- Steel and Iron: These harder materials require a more robust wire cutter, often with hardened steel blades.
- Plastic-Coated Wires: If you’re cutting wires with a plastic coating, you’ll need a cutter that can handle the additional thickness without crushing the wire.
b. Size and Gauge of the Wire
Wire size and gauge play a critical role in determining the appropriate cutter. A wire cutter must be able to handle the thickness of the wire:
- Small Gauge Wires: For thinner wires, a pair of precision wire cutters or diagonal wire cutters will suffice.
- Large Cables: For thicker cables, such as those used in industrial applications, a cable cutter with a ratcheting mechanism is ideal.
c. Comfort and Ease of Use
Comfort is essential, especially if you’ll be using the wire cutter for extended periods. Look for cutters with ergonomic handles that reduce hand fatigue:
- Handle Design: Handles should fit comfortably in your hand and provide a good grip. Rubberized or padded handles can enhance comfort.
- Spring Mechanism: A spring-loaded mechanism can make repetitive cutting tasks easier by reducing the effort needed to open the cutter after each cut.
d. Safety Features
Safety should always be a priority when using tools. Consider wire cutters with the following safety features:
- Non-Slip Grips: Ensure the handles have non-slip grips to prevent accidental slips during use.
- Locking Mechanism: A lockable handle is useful for keeping the cutter closed when not in use, reducing the risk of accidental cuts.
- Insulated Handles: For electrical work, choose wire cutters with insulated handles to protect against electric shocks.
4. Top Brands and Models of Wire Cutters
When investing in a wire cutter, it’s essential to choose a reputable brand that offers durability, precision, and reliability. Here are some of the top brands and models available on the market:
a. Klein Tools
Klein Tools is a well-known brand in the electrical and construction industries, known for its high-quality tools. Their wire cutters are durable and precise, making them a favorite among professionals.
Popular Models:
- Klein Tools D228-8: A versatile diagonal cutting plier that offers excellent cutting performance for small gauge wires.
- Klein Tools 63050: A cable cutter designed to handle larger cables with ease, featuring precision ground, hardened blades for clean cuts.
b. Irwin Vise-Grip
Irwin Vise-Grip offers a range of wire cutters with ergonomic designs and strong cutting power. These cutters are popular among both professionals and DIYers.
Popular Models:
- Irwin Vise-Grip 2078309: A diagonal cutting plier with induction-hardened cutting edges, perfect for cutting a variety of wire types.
- Irwin Vise-Grip 1866073: A high-leverage cable cutter designed for cutting thicker cables with less effort.
c. Channellock
Channellock is known for its rugged construction and long-lasting performance. Their wire cutters are built to withstand tough jobs, making them a reliable choice for professionals.
Popular Models:
- Channellock 338: A diagonal cutting plier with a strong, durable design, ideal for cutting wires in various applications.
- Channellock 911: A cable cutter with a high-leverage design, capable of cutting through tough cables with ease.
d. Knipex
Knipex is a German brand renowned for its precision and high-quality materials. Their wire cutters are often used in delicate electronic work, where precision is paramount.
Popular Models:
- Knipex 74 01 250: A heavy-duty diagonal cutter with high cutting performance, suitable for cutting hard wires and cables.
- Knipex 95 61 190: A cable cutter designed for clean and precise cuts on cables up to 15mm in diameter.
5. Proper Usage of Wire Cutters
Using a wire cutter correctly ensures safety and prolongs the life of the tool. Here are some tips on how to use wire cutters effectively:
a. Select the Right Tool for the Job
Always choose a wire cutter that is appropriate for the material and thickness of the wire you are cutting. Using the wrong tool can result in a poor cut, damage to the tool, or even injury.
b. Ensure a Firm Grip
Hold the wire cutter with a firm grip, ensuring that your hand is comfortable and stable. A steady grip allows for precise cuts and reduces the risk of the cutter slipping.
c. Position the Wire Correctly
Place the wire as close to the pivot point of the cutting edges as possible. This position provides the most cutting power and ensures a clean, smooth cut.
d. Apply Even Pressure
Squeeze the handles evenly and firmly to cut through the wire. Avoid jerking or twisting the cutter, as this can damage the tool and result in an uneven cut.
e. Clean Up After Each Cut
After cutting, remove any small pieces of wire or debris from the cutting edges. This practice keeps the cutter in good condition and prevents any obstructions during the next cut.
6. Maintenance and Care of Wire Cutters
Proper maintenance of wire cutters is essential for ensuring their longevity and performance. Regular care will keep your tool in top condition and ready for any task.
a. Cleaning and Oiling
After each use, clean the wire cutter to remove any dirt, debris, or metal shavings that may have accumulated. Use a soft cloth to wipe down the cutting edges and handles. If the cutter has a pivot point, apply a small amount of oil to keep it moving smoothly.
Steps for Cleaning:
- Wipe Down the Blades: Use a soft, dry cloth to remove any dirt or debris from the blades.
- Apply Oil: Apply a drop of light machine oil to the pivot point and moving parts.
- Wipe Excess Oil: After applying oil, wipe off any excess to prevent it from attracting dust.
b. Proper Storage
Store wire cutters in a dry, cool place to prevent rust and corrosion. If possible, keep them in a tool box or pouch to protect them from moisture and dust. Avoid leaving them exposed to the elements, especially in damp or humid environments.
c. Sharpening the Cutting Edges
Over time, the cutting edges of a wire cutter may dull, reducing its effectiveness. Regular sharpening can restore the edges to their original sharpness. Use a fine file or sharpening stone to sharpen the blades, following the manufacturer’s guidelines.
Sharpening Tips:
- Secure the Cutter: Hold the cutter securely in a vice or with a clamp to prevent it from moving during sharpening.
- Sharpen Evenly: Apply the file or stone evenly across the cutting edge, maintaining the original angle of the blade.
- Test the Cut: After sharpening, test the cutter on a piece of wire to ensure it is sharp and cutting cleanly.
d. Inspect for Wear and Tear
Regularly inspect your wire cutter for signs of wear and tear. Check the handles for cracks or damage, and ensure the cutting edges are sharp and free of nicks. If the cutter is showing significant signs of wear, consider replacing it to avoid potential injury.
7. Common Mistakes to Avoid with Wire Cutters
To get the most out of your wire cutter and ensure your safety, it’s important to avoid common mistakes. Here are some pitfalls to watch out for:
a. Using the Wrong Cutter for the Wire Type
Using a wire cutter that is not designed for the material or thickness of the wire can result in a poor cut, damage to the cutter, or injury. Always match the cutter to the wire you are working with.
b. Overexerting the Tool
Applying excessive force to cut through a wire can damage the cutter and result in an uneven cut. If you find yourself struggling to cut through a wire, you may be using the wrong tool. Consider switching to a cutter that is better suited to the task.
c. Neglecting Maintenance
Failing to clean and oil your wire cutter can lead to rust, corrosion, and reduced performance. Regular maintenance is essential for keeping your cutter in top condition and ensuring it performs well over time.
d. Using Wire Cutters on Non-Metal Materials
Wire cutters are designed specifically for cutting metal wires and cables. Using them on non-metal materials, such as plastic or wood, can damage the cutting edges and reduce the tool’s effectiveness.
8. Applications and Industries that Rely on Wire Cutters
Wire cutters are used in a variety of industries, each with its unique demands. Here’s a look at some of the key industries that rely heavily on wire cutters:
a. Electrical Work
In electrical work, wire cutters are essential for cutting, stripping, and trimming wires during installations and repairs. Electricians often use diagonal wire cutters for precision cuts and cable cutters for larger cables.
b. Crafting and Jewelry Making
Artists and crafters use wire cutters to manipulate wire for jewelry making, sculpture, and other creative projects. Precision wire cutters are often preferred for these tasks due to their ability to make clean, precise cuts on thin wires.
c. Automotive Repair
Mechanics use wire cutters to work on vehicle wiring systems, especially when dealing with electrical components. Cable cutters are commonly used to cut through thicker wires and cables found in automotive applications.
d. Construction and Rigging
In construction, wire cutters are used to cut rebar ties, mesh, and other metal components. Rigging professionals also rely on wire rope cutters to trim wire ropes used in lifting and securing loads.
e. Telecommunications
Telecommunications professionals use wire cutters to install and maintain communication lines, including telephone, internet, and fiber optic cables. Precision cutters are essential for handling the delicate wires used in these applications.
9. Innovations in Wire Cutter Technology
The basic design of wire cutters has remained relatively unchanged over the years, but there have been several innovations that have enhanced their performance and usability:
a. Ergonomic Design
Modern wire cutters feature ergonomic designs that reduce hand fatigue and improve grip. These advancements are particularly beneficial for professionals who use the tool for extended periods.
b. Insulated Handles
For those working with electrical wires, insulated handles provide added protection against electric shocks. These handles are designed to meet specific safety standards and offer peace of mind during electrical work.
c. Ratcheting Mechanisms
Ratcheting mechanisms in cable cutters allow for easier cutting of thick cables. This feature reduces the amount of force needed and provides a cleaner, more controlled cut.
d. High-Tech Materials
Wire cutters are now being made with high-tech materials, such as titanium-coated blades and reinforced steel, to enhance durability and cutting performance.
10. Conclusion: The Importance of Choosing the Right Wire Cutter
A wire cutter is a vital tool in many industries, offering the precision and efficiency needed to handle various tasks. Whether you’re cutting small gauge wires in electronics or large cables in construction, choosing the right wire cutter is crucial for success.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the different types of wire cutters, how to select the best one for your needs, the top brands and models, and tips for proper usage and maintenance. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your wire cutter remains in top condition and continues to perform at its best.
Remember, investing in a high-quality wire cutter from a reputable brand like Klein Tools, Irwin Vise-Grip, Channellock, or Knipex is a wise decision. These tools are designed to withstand the rigors of regular use and provide clean, accurate cuts every time.
Whether you’re a professional electrician, a mechanic, a crafter, or simply a DIY enthusiast, having the right wire cutter can make all the difference in the success of your project. Take the time to choose the best tool for your needs, maintain it properly, and you’ll enjoy years of reliable service from your wire cutter.
By understanding the various options available and how to care for your tool, you can make the most of your wire cutter and ensure that it serves you well in all your cutting tasks.