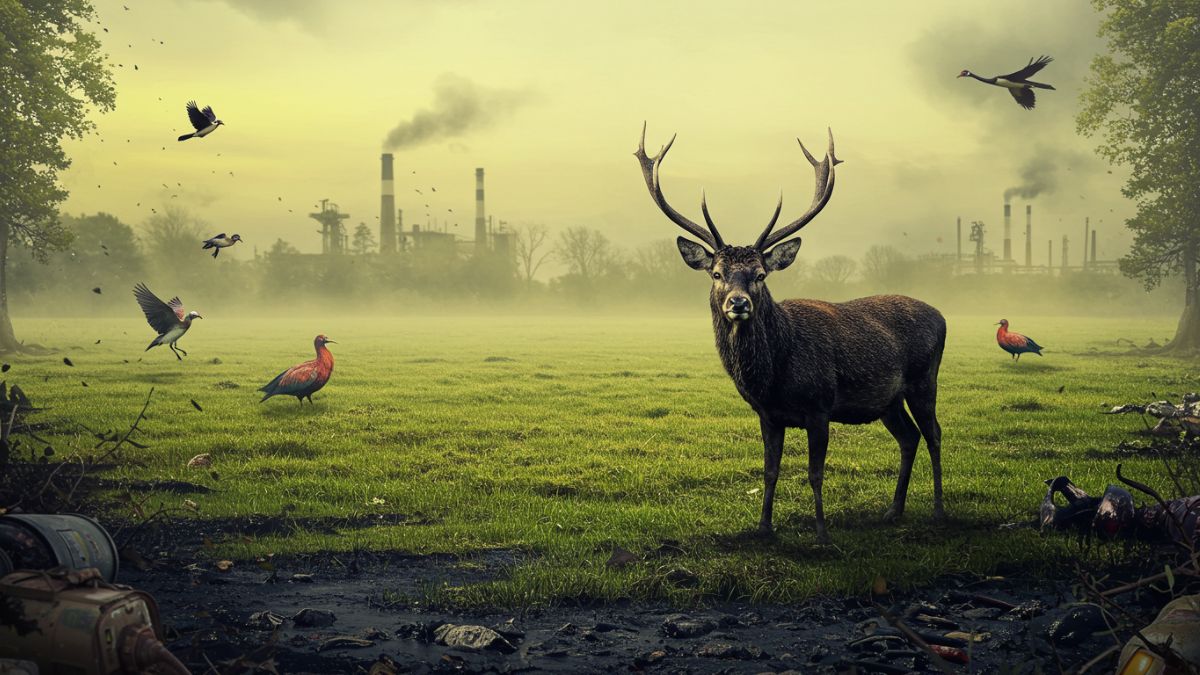
Pollution has become one of the most significant threats to wildlife “animals pollution” and ecosystems, altering habitats and endangering species across the globe. From plastics in the ocean to pesticides in farmlands, pollutants are infiltrating every corner of the natural world, leaving devastating consequences in their wake.
This blog will explore how pollution is harming animals and ecosystems, focusing on various types of pollution, their impact, and actionable steps to mitigate these effects. The goal is to shed light on this pressing issue and inspire individuals and organizations to take meaningful action.
Types of Pollution Affecting Wildlife and Ecosystems
Pollution comes in many forms, each with its unique impact on animals and ecosystems. Here are some key types of pollution wreaking havoc on the natural world:
1. Plastic Pollution
Plastic pollution is one of the most widespread environmental issues. With billions of tons of plastic waste entering landfills and waterways each year, its impact on wildlife is catastrophic.
- Impact on Marine Life: Marine animals often mistake plastic debris for food, leading to entanglement, ingestion, and ultimately death. Sea turtles, for instance, mistake plastic bags for jellyfish, while seabirds are found with stomachs full of plastic fragments.
- Ecosystem Disruption: Microplastics—tiny plastic particles—are ingested by small marine organisms that form the base of the food chain, affecting predators higher up, including humans.
2. Chemical Pollution
Toxins from industrial waste, pesticides, and agricultural runoff are severely impacting the health of animals and ecosystems.
- Impact on Wildlife: Pesticides like neonicotinoids have been linked to declining bee populations, which affects pollination and the overall health of ecosystems. Heavy metals such as mercury and lead poison fish, birds, and mammals, accumulating in their bodies over time.
- Long-term Damage: When these chemicals enter water bodies, they can create “dead zones” where oxygen levels are too low to support aquatic life.
3. Air Pollution
Airborne pollutants from factories, vehicles, and agricultural activities contribute to poor air quality, directly impacting wildlife and plant life.
- Respiratory Issues in Animals: Just like humans, animals exposed to air pollution can develop respiratory diseases, including asthma and bronchitis.
- Habitat Loss: Acid rain, formed by pollutants like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide, damages forests and freshwater ecosystems, eroding habitats critical for countless species.
4. Noise Pollution
While often overlooked, noise pollution from urban development, highways, and industrial activities is increasingly disrupting natural habitats.
- Impact on Behavioral Patterns: Many animals rely on sound for communication, navigation, and hunting. For example, whales and dolphins are severely impacted by underwater noise from shipping and drilling activities.
- Disrupted Ecosystems: Noise pollution can push wildlife away from their natural habitats, altering predator-prey dynamics and threatening biodiversity.
5. Light Pollution
Excessive artificial lighting from cities and industrial areas is disorienting for many species.
- Disorientation in Animals: Nocturnal species that rely on darkness for foraging or escaping predators are particularly vulnerable. For instance, baby sea turtles become confused by bright city lights, moving away from the ocean instead of towards it.
- Impact on Ecosystems: Light pollution can disturb the natural rhythms of plants and animals, reducing reproductive success rates and altering entire ecosystems.
The Ripple Effect on Ecosystems
Pollution doesn’t just affect individual species—it has a cascading impact on entire ecosystems. When a key species suffers due to pollution, the balance of the ecosystem begins to collapse. For instance:
- Declining bee populations caused by pesticide use lead to reduced pollination, directly affecting crop yields and plant biodiversity.
- Coral bleaching, exacerbated by water pollution and climate change, disrupts marine ecosystems that depend on healthy reefs for survival.
- Chemicals in the food chain can lead to biomagnification, where toxins concentrate in predators at the top, such as eagles or polar bears, threatening their survival.
Real-World Examples of Pollution’s Impact
The Great Pacific Garbage Patch
This infamous floating mass of plastics in the Pacific Ocean spans more than 600,000 square miles. Marine life living in these waters faces constant threats from entanglement and ingestion of plastics, leading to injury or death.
The Aral Sea Crisis
Once the fourth-largest lake in the world, the Aral Sea in Central Asia has been drastically reduced due to agricultural chemical runoff and diversion of water. This destruction has had severe consequences for local fish populations and bird species that relied on the lake.
The Decline of Amphibians
Amphibians, particularly frogs and salamanders, are declining worldwide due to chemical runoff from pesticides. Their porous skin makes them specifically vulnerable to pollution, marking them as one of the most affected animal groups.
What Can Be Done?
The fight against pollution requires collective action. Governments, organizations, and individuals all have roles to play. Here are a few actionable steps to help mitigate the impact of pollution on wildlife and ecosystems:
1. Adopt Sustainable Practices
- Reduce, reuse, recycle plastics to minimize plastic pollution.
- Support sustainable agriculture practices to limit chemical pollution.
- Conserve energy to reduce emissions contributing to air pollution and acid rain.
2. Advocate for Policy Changes
Legislation is a powerful tool against pollution:
- Advocate for stricter regulations on industrial emissions and waste disposal.
- Support bans on single-use plastics and harmful pesticides.
- Promote policies encouraging renewable energy use.
3. Participate in Conservation Efforts
Get involved in local or global efforts to combat pollution:
- Join beach and community clean-up events.
- Support organizations working to conserve endangered species and habitats.
- Donate to reputable environmental charities actively working on pollution mitigation.
4. Educate and Raise Awareness
Education is key to solving the pollution crisis. Spread information about the impact of pollution on wildlife and ecosystems through social media, schools, and community events to inspire others to take action.
5. Choose Eco-Friendly Products
Switch to products made with biodegradable or eco-friendly materials to reduce personal environmental impact. For example, opt for natural fertilizers over chemical ones or reusable items instead of single-use plastics.
Make a Difference Today
The impact of pollution on wildlife and ecosystems is dire, but it’s not too late to reverse the damage. By reducing pollution at its source, advocating for change, and adopting sustainable practices, we can protect the balance of our planet’s ecosystems.
Every action, no matter how small, contributes to a larger goal. Start by making mindful choices in your daily life, educating others, and supporting organizations working to combat pollution. Together, we can ensure a healthier future for all species.
Conclusion
The responsibility to protect our environment lies with each of us, and the time to act is now. Through informed decisions, sustainable habits, and collective efforts, we can mitigate the effects of pollution and safeguard the planet’s resources for generations to come. Remember, every choice matters. By embracing eco-conscious practices, we become part of the solution, fostering a cleaner, greener world where both people and nature can thrive
FAQs
What are the main types of pollution affecting the environment?
The primary types of pollution include air pollution, water pollution, soil contamination, and noise pollution. Each type disrupts ecosystems and poses significant health risks to humans and wildlife.
How can individuals reduce their contribution to pollution?
Individuals can reduce pollution by adopting sustainable practices such as recycling, reducing single-use plastics, using public transportation, conserving water, and supporting clean energy solutions. Small lifestyle changes can collectively lead to significant environmental benefits.
What role does education play in combating pollution?
Education is pivotal in raising awareness about pollution and its impact. By educating communities, we empower individuals to make informed decisions, adopt greener habits, and advocate for policies that protect the environment.
Why is it important to act now?
Pollution has reached critical levels, threatening ecosystems, human health, and the planet’s future. Immediate action is essential to mitigate these effects, prevent further damage, and ensure a habitable world for current and future generations.
How do organizations contribute to reducing pollution?
Organizations lead initiatives to clean up polluted areas, promote sustainable development, and advocate for stricter environmental regulations. By supporting these organizations, individuals can amplify efforts to combat pollution on a larger scale.