Intriguing and remarkably beautiful, the cross fox is an animal that captures the attention and curiosity of wildlife enthusiasts and casual nature observers alike. But what exactly is a cross fox? How does it differ from its better-known relatives, and where can you find it in the wild? This blog will guide you through everything you need to know about the cross fox, from its physical traits to its natural habitat and behaviors.
What is a Cross Fox?
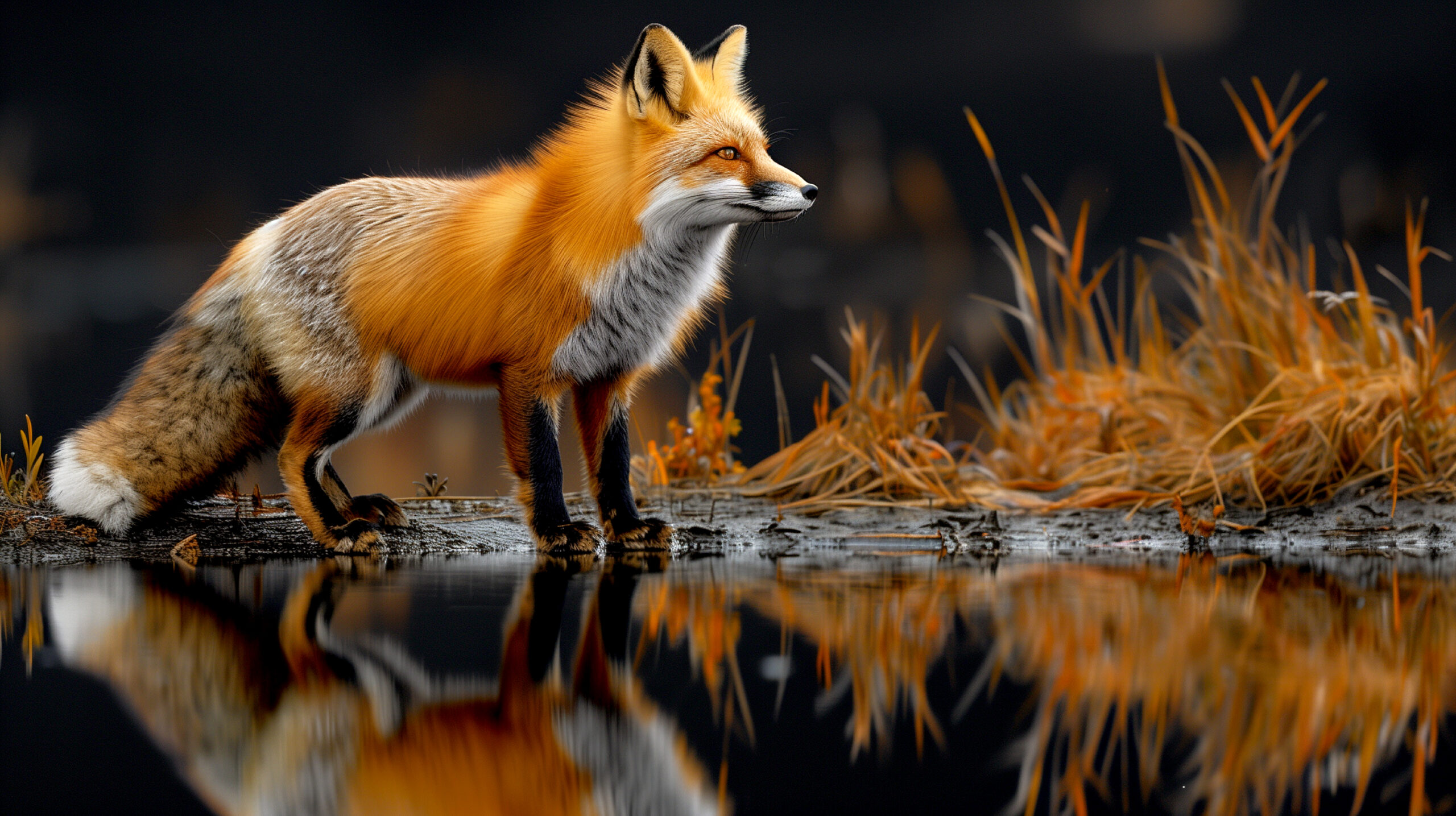
The cross fox is a color variant of the red fox (Vulpes vulpes), one of the most widely distributed and recognizable members of the Canidae family. While it isn’t a separate species or subspecies, it stands out because of its striking appearance. Its name derives from the dark stripe running along its back, which intersects with another stripe across its shoulders, forming a cross-like shape.
Though less common than standard red foxes, cross foxes are not exceedingly rare. Their unique coloration appears as a result of genetic variation, specifically within the same species, and they are most often found in regions where red fox populations thrive.
Key Traits of a Cross Fox
Cross foxes possess many of the same physical characteristics as the red fox but can be easily distinguished by their distinctive coloring and markings. Here’s a closer look at the traits that set them apart:
1. Unique Fur Coloring
The most striking feature of a cross fox is its fur. The coat typically combines shades of reddish-brown, black, and gray in a gradient effect. The deep black cross marking on their back and shoulders serves as the key identifying trait.
These darker markings tend to blend into black legs, and some individuals may have pale facial markings contrasting with their darker midsection. The richness and depth of their coloring also give them a “smoldering” or dusky appearance, which often draws admiration.
2. Size and Build
Cross foxes are slightly larger than typical red foxes. They typically weigh between 10 to 15 pounds, with their length (including their bushy tail) ranging from 35 to 50 inches. Similar to their red fox relatives, they have sharp, triangular ears and a narrow snout.
3. Adaptability
Like other members of the species, cross foxes are incredibly adaptable. They thrive in various climates and terrains, exhibiting physical and behavioral traits that make them proficient hunters and survivors in the wild.
Habitat and Distribution
Cross foxes inhabit many of the same regions as red foxes, although they are much less common. They are primarily found in North America and some parts of Europe and Asia. Certain Canadian provinces and northern U.S. states have recorded higher proportions of cross fox populations compared to other regions.
1. Preferred Habitat
Cross foxes tend to reside in mixed forests, tundras, and grasslands, favoring areas with abundant prey and cover. They are adaptable enough to survive in almost any environment where red foxes thrive, including urban and suburban areas, though the latter is uncommon.
2. Geographic Range
The presence of cross foxes is especially notable in Canada, particularly in regions such as Alberta and Manitoba. While they are spotted in some U.S. states, sightings are relatively rare and usually confined to areas with colder climates.
Diet and Hunting Behavior
Similar to red foxes, cross foxes are omnivorous animals with highly versatile diets. They are opportunistic hunters, meaning they will eat whatever food sources are most readily available to them.
Primary Diet
- Small Mammals: Rabbits, rodents, and other small mammals are staples of their diet.
- Birds and Eggs: Cross foxes occasionally hunt birds or raid nests for eggs.
- Fruits and Vegetation: Depending on the season, they consume various fruits, berries, and even grains.
- Scavenging: Cross foxes won’t shy away from scavenging. They are experts at locating leftover meals from other predators or food discarded by humans.
Hunting Techniques
Cross foxes exhibit agility and stealth in their hunting practices. They rely on their keen senses of hearing and smell to locate prey. A common hunting behavior includes leaping into the air to pounce on unsuspecting prey hidden in grass or snow.
Mating and Social Behaviors
Cross foxes share many behavioral traits with red foxes, particularly in terms of mating habits and family dynamics.
1. Mating Season
The cross fox’s mating season occurs during late winter, generally between January and March. Like other foxes, they are monogamous, often forming pair bonds that last for one breeding season or longer.
2. Raising Kits
A typical litter consists of 4-6 kits, which both parents work together to raise. During this time, the mother remains at the den to care for the kits while the father hunts and brings back food.
3. Communication
Cross foxes are vocal creatures. Beyond their characteristic barks, they also use a range of unique calls, whines, and growls to communicate with each other, especially when marking their territory or alerting others to danger.
Conservation and Environmental Role
While cross foxes are not classified as endangered, their specific habitat should still be protected to maintain a thriving ecosystem. Foxes, including the cross fox variety, play a vital role as both predator and prey in their environments, contributing to balanced populations of rodents and other small animals.
It is important for conservation efforts to focus on preserving the broader habitats cross foxes depend on. Deforestation, urbanization, and climate change all present potential threats to these ecosystems, which could ultimately impact cross fox populations even in stable regions like Canada.
Fascinated by Cross Foxes? Venture Further
Cross foxes provide a fascinating window into the diversity and adaptability of the red fox species. From their striking appearance to their remarkable survival skills, these animals continue to capture imaginations around the globe. Observing or learning more about cross foxes is not only a reminder of nature’s beauty but also a call to appreciate and preserve the delicate ecosystems they inhabit.
If you’re interested in wildlife and want to explore more captivating topics like this, subscribe to our blog or follow [Organization/Platform Name] for regular updates.
Final Thought
The cross fox stands as a testament to the resilience and beauty of the natural world. By understanding and appreciating species like this, we deepen our connection to the environment and recognize the importance of conservation efforts. Protecting these unique creatures and their habitats ensures that future generations can continue to marvel at their elegance and complexity. Every small action toward preserving the natural world makes a meaningful difference—together, we can secure a thriving planet for all living beings.
Conclusion
The wonders of nature never cease to amaze, and creatures like the cross fox are powerful reminders of the intricate balance that sustains life on Earth. By fostering awareness, supporting conservation initiatives, and advocating for environmental preservation, we hold the key to safeguarding the extraordinary diversity of our planet. Each step taken, no matter how small, brings us closer to a future where humans and wildlife coexist harmoniously. Together, we can champion a legacy of care and stewardship for generations to come.
FAQs
1. Why is conservation important for biodiversity?
Conservation is vital for maintaining biodiversity, as it ensures the survival of diverse species and the ecosystems they inhabit. Biodiversity supports essential environmental processes, such as pollination, water purification, and climate regulation, which are critical for all life on Earth. Protecting habitats and species helps preserve this delicate balance and prevents irreversible loss.
2. How can individuals contribute to conservation efforts?
Individuals can make meaningful contributions by supporting conservation organizations, reducing waste, using sustainable products, and spreading awareness about environmental issues. Simple actions, such as planting native plants or limiting single-use plastics, can collectively have a significant positive impact.
3. What is the role of education in environmental protection?
Education plays a key role in fostering environmental stewardship. By learning about ecosystems, species, and conservation challenges, individuals are empowered to make informed decisions and advocate for sustainable practices. Educating the younger generation ensures they inherit the knowledge and responsibility to protect the planet.
4. How does climate change affect wildlife and ecosystems?
Climate change disrupts ecosystems through rising temperatures, habitat loss, and extreme weather events, causing stress for many species. These changes can lead to migration, loss of food sources, and even extinction, making it crucial to address climate change to protect wildlife and their environments.
5. What are the benefits of preserving endangered species?
Preserving endangered species goes beyond protecting animals; it benefits ecosystems, cultural heritage, and economies. Many species play indispensable roles in their habitats, and their loss can lead to cascading ecological effects. Conservation also upholds the intrinsic value of wildlife and strengthens the connection between nature and humanity.